Describe the Tissue of the Heart Valves
Chambers of the Heart The internal cavity of the heart is divided into four chambers. Heart valves HVs are cardiac structures whose physiological function is to ensure directed blood flow through the heart over the cardiac cycle.
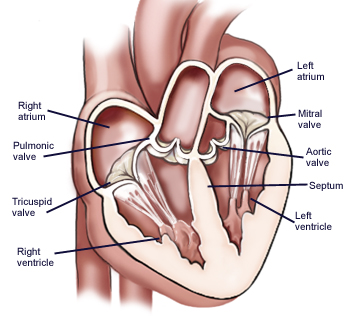
4 Valves Of The Heart What Are They How They Work
Right atrium Right ventricle Left atrium Left ventricle.
. This can lead to arrhythmia which refers to an abnormal heart rate or. The valves prevent the backward flow of blood. The valves open or close each.
The heart wall consists of three layers enclosed in the pericardium. A heart valve opens or closes according to differential blood pressure on each side. One is located at each.
Three layers of tissue form the heart wall. Describe the internal anatomy of the heart including the chambers and valves and relate the internal features to how it functions as a pump. There are two atrioventricular AV valves.
Four valves enforce the one-way traffic. While primarily passive structures that are driven by forces exerted by the surrounding blood and heart this description does not adequately describe their elegant and complex biomechanical function. It is one of two atrioventricular valves meaning that it is located between the atrium and the ventricle in this case on the right side of the heart.
The four valves in the mammalian heart are two. Tricuspid Valve Has three leaflets or cusps. Four valves maintain the unidirectional flow of blood through the heart.
Both types of valve tissues are also treated with various other chemical agents to minimize their propensity to calcify over the duration of implantation and hence improve their longevity. These valves are actual flaps that are located on each end of the two ventricles lower chambers of the heart. There is a valve through which blood passes before leaving each chamber of the heart.
The valves are located between the atria and ventricles and in the two arteries that empty blood from the ventricles. Sometimes the tricuspid valve doesnt function properly for example tricuspid regurgitation and tricuspid stenosis. Blood passes through a valve before leaving each chamber of the heart.
Describe the coverings the surface anatomy and tissue layers of the heart. The valves are made of strong thin flaps of tissue called leaflets or cusps. The tricuspid valve is the first valve that blood flows through in the heart.
In heart valve tissue engineering nanofibrous scaffolds should be able to provide a suitable atmosphere for cell growth if they can form three dimensional assemblies with fiber diameter porosity and mechanical properties similar to natural heart valves 147. The valves prevent the backward flow of blood. The cardiac muscle tissue of your right ventricle is replaced with fatty or fiber-rich tissue.
A middle concentric layer. The tricuspid valve is one of four heart valves. Signaling pathways have critical functions in primary.
They are composed mostly of fibrous connective tissue that extends from the heart walls. 42 The homograft valves are intact human valves obtained from organ and tissue donors usually stored cryopreserved as entire aortic or pulmonary roots and trimmed to size and shape before. From the atria to the ventricles and out the great arteries leaving the superior aspect of the heart.
They open and close in response to differences in blood pressure. The external surfaces of the valves. The four valves of the heart.
The human heart is located within the thoracic cavity medially. Our heart has four valves one for each chamber of the heart. The outer layer of the heart wall is the epicardium the middle layer is the myocardium and the inner layer is the endocardium.
A heart valve is a one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. Normal valves have 3 flaps leaflets except the mitral valve. It only has 2 flaps.
Currently there are over a quarter of a million prosthetic heart valves implanted annually and the number of patients requiring replacement surgeries is only suspected to rise and even triple over the next. These four heart valves decide the pathway for efficient blood flow through the. The 4 heart valves are.
The leaflets open to let blood move forward through the heart during half of the heartbeat. Location and Size of the Heart. A normal healthy heart valve minimizes any obstructions and allows the blood to flow smoothly and freely.
Valves open or close based on pressure differences across the valve. It is made of three flaps or leaflets that work together to stop and start the flow of blood. Myocardium - the muscular middle layer of the wall of the heart and has excitable tissue and the conducting system.
The heart consists of four chambers two atria upper chambers and two ventricles lower chambers. It helps blood flow in the correct direction from the right atrium to the right ventricle. They close to keep blood from flowing backward during the other half of the heartbeat.
The condition may need to be monitored or you may require valve repair or replacement. Trace the coronary circulation and explain why this ciruclation is needed. What are heart valves.
Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. The bicuspid valve that divides the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart A heart valve allows blood flow in only one direction through the heart and the combination of the atrioventricular and semi-lunar heart valves determines the pathway of blood flow. Blood flows through the heart in one direction.
The mature heart valves are made up of highly organized extracellular matrix ECM and valve interstitial cells VIC surrounded by an endothelial cell layer. Separates the top right chamber right atrium from the bottom right chamber right ventricle. Prevents the back flow of blood from the right ventricle to the right atrium.
Greater surface area to volume ratios high porosity and small fiber diameters of scaffolds mimic the ECM therefore. What are heart valves. Tissue engineered heart valves offer a new and advancing proposed treatment of creating a living heart valve for people who are in need of either a full or partial heart valve replacement.
The four valves of the heart allow blood into the heart and prevent it from flowing in the wrong direction. Opens to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle. Epicardium - the outer layer of the wall of the heart and is formed by the visceral layer of the serous pericardium.
The ECM of the valves is stratified into elastin- proteoglycan- and collagen-rich layers that confer distinct biomechanical properties to the leaflets and supporting structures. Valves are actually flaps leaflets that act as one-way inlets for blood coming into a ventricle and one-way outlets for blood leaving a ventricle. However in the case of the heart it is not a microscopic layer but rather a macroscopic layer consisting of a simple squamous epithelium called a mesothelium reinforced with loose irregular or areolar connective tissue that attaches to the pericardium.
The four valves in order of circulation are. These tissue-paper thin membranes attached to our heart walls open and close to regulate blood flow.
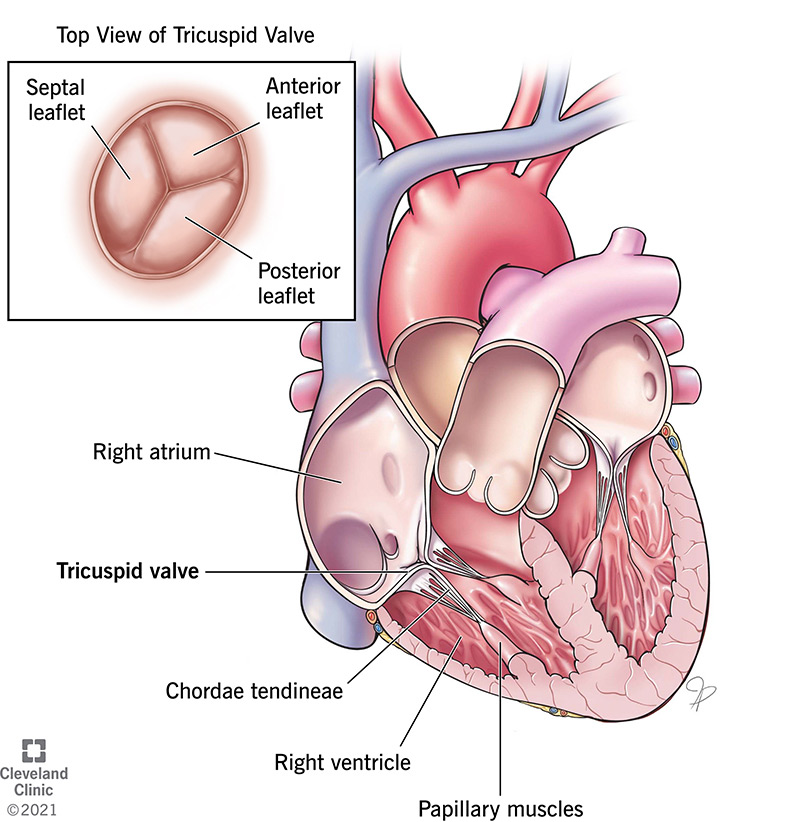
Tricuspid Valve Overview Function And Anatomy
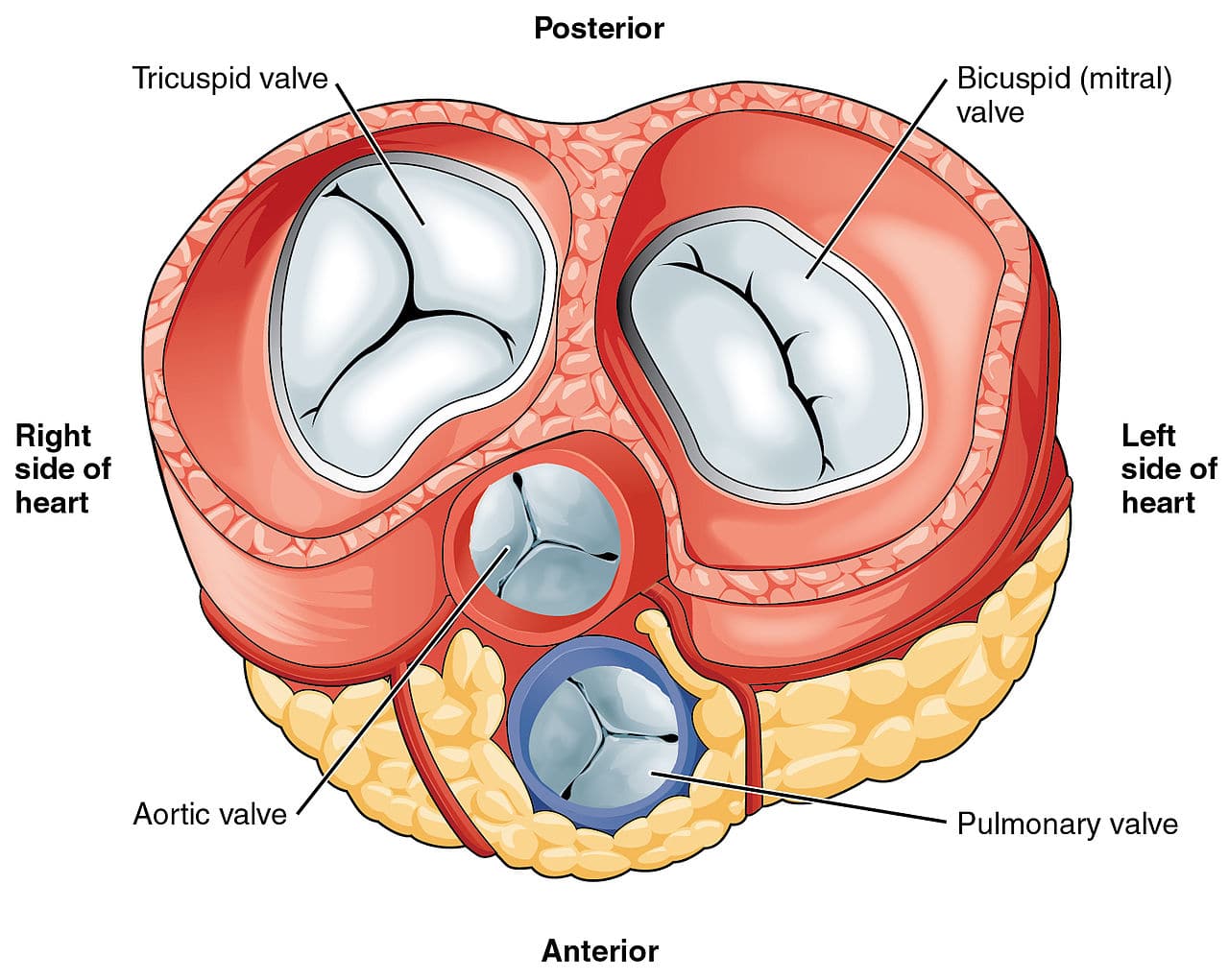
The Heart Valves Tricuspid Aortic Mitral Pulmonary Teachmeanatomy
Schematics Of Heart Valve Anatomy A The Arrangement Of The Valves In Download Scientific Diagram

No comments for "Describe the Tissue of the Heart Valves"
Post a Comment